Skew Lognormal Cascade Distribution
Tail risk is omnipresent
[].
Our world is more volatile than we want to admit...
Let's navigate the world of Fat Tails []
(aka Heavy Tails [])
beyond normal distribution
|
|
This website is set up to present the Skew Lognormal Cascade Distribution,
proposed by Stephen Lihn in 2008; and subsequently Poisson Subordinated Distribution in 2012.
More and more evidences tell us that tail risk is omnipresent (it is everywhere, universal).
With this distribution, a large portion of the tail risk in the financial market can be
quantitatively measured.
This distribution exhibits fat-tail, asymmetry tunable by a skew parameter,
converges to normal distribution, and has finite moments.
These fine properties make it very useful in financial applications..
More materials will be posted here, including papers, charts, remos, implementations, etc. Stay tuned.
One of the most urgent topics is to combine this distribution with a double-Perato distribution.
|
Summary: |
| Stochastic Equation: |
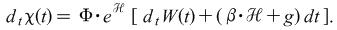 where
where
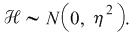 |
| Static Distribution: |
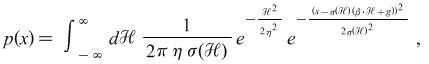
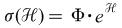
The symmetric form is identical to the result of
P. K. Clark's lognormal subordinated Levy process.
|
Scaling And Equilibrium In The Stock Market |
|
The N^3/2 Law is a new finding. The size of the stock market follows a law of f(N),
which is not Sarnoff's, nor Metcalfe's, nor Reed's. |
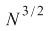 Scaling Law: Scaling Law:
[Full Wiki]
|
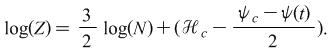 |
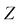 : Total market value, : Total market value,
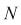 : Number of stocks, : Number of stocks,
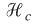 : Logarithmic mean of capital distribution : Logarithmic mean of capital distribution
|
| Optimal Volatility Equilibrium: |
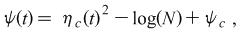 |
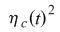 : Variance of capital distribution : Variance of capital distribution
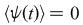 : Mean reverting volatility : Mean reverting volatility |
Market Process:
(Volatility) |
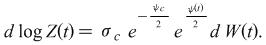 |
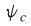 : Capital Distribution Constant : Capital Distribution Constant
|
|
The plot shown below is the skew distribution that approximately describes
(1) The time-series return distribution of Dow Jones Industrial Average over 80 years;
(2) The return distribution of the stocks in the entire market universe.
Click on the plot to see more details about the distribution.
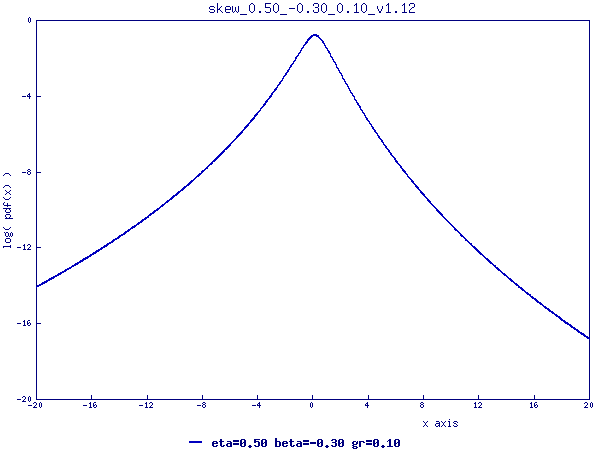
|
Working Papers on SSRN
2012:
Abstract
A new Poisson subordinated distribution is proposed to capture major
leptokurtic features in log-return time series of financial data. This
distribution is intuitive, easy to calculate, and converge quickly. It
fits well to the historical daily log-return distributions of
currencies, commodities, Treasury yields, VIX, and, most difficult of
all, DJIA. It serves as a viable alternative to the more sophisticated
truncated stable distribution.
keywords: Subordination, Poisson, financial data, fat tail, leptokurtotic
2010:
Abstract
This working paper is an excerpt on the recent finding of the network
effect in the stock market. Specifically I summarize the three-half
power law which states that the total value of the stock market
is proportional to the three-half power of the number of stocks in the
market. This power law is based on several intuitive assumptions on a
many-body stochastic
system, which will be described in this paper. The hypothesis of the
optimal volatility equilibrium is introduced as a pillar leading to the
power law,
which states that such system must adjust itself around a level of
optimal volatility in order to survive as a viable market.
The connections to Fernholz's diversity index and Clark's lognormal
subordinated process are discussed.
This hypothesis also indicates that investing in a large market doesn't
guarantee the "benefit" of diversification as prescribed in modern
portfolio theory.
keywords: network effect, volatility, lognormal cascade, fat tails, heavy tails, stochastic portfolio theory
(
C)
2010:
keywords: P. K. Clark, subordinated process, lognormal cascade distribution
(
C,
Clark, 1973)
2009:
Abstract
This working paper presents the general theory of the higher order
"skew lognormal cascade distribution" as a mathematical extension of
the previously proposed skew lognormal cascade distribution.
In particular, the second order distribution is studied in details,
which incorporates the fat tails into the volatility (aka the
volatility of volatility). We show that the second order distribution
can handle very heavy tails and high kurtosis in the high frequency
financial time series.
It accurately fits the daily log-returns of Dow in 80 years, whose
kurtosis is 26.
The framework of the higher order lognormal cascade distributions also
provides a new way to study the capital distribution (aka firm size
distribution), the market index, and the market entropy of the stock
market.
Such study in the context of stochastic portfolio theory reveals that
the origin of the fat tails in the fluctuations of the market index is
from the lognormal cascade structure of the capital distribution in the
market.
We show from a simple stochastic model that the contraction and
expansion of the underlying capital distribution is the fundamental
driving force of the bull-bear market cycles and the market volatility
in the past 20 years.
A stochastic equation is derived to establish the relation between the
market index and the capital distribution, which is the lognormal
cascade equation in our theory.
This shows that the fluctuations of the market index are a natural
mathematical consequence of the stochastic calculus on the market
portfolio in which weights are exponentially distributed.
Therefore, we conclude that the phenomena of fat tails should exist
everywhere in our financial system.
keywords: lognormal cascade, fat tails, heavy tails, capital distribution, time series, stochastic portfolio theory
(
C)
2008:
Abstract
A continuous-time scale-invariant Brownian motion (SIBM) stochastic
equation is developed to investigate the dynamics of the stock market.
The equation is used to solve the fat tail distribution of the stock
universe and the DJIA time series. It is also used to model the
volatility clustering in the DJIA time series. The equation is
transformed from the Langevin equation into a fractal expression
involving an infinite array of random walk.
It predicts an elegant way of generating the skew form of the lognormal
cascade distribution (Kolmogorov and Mandelbrot), which describes the
static log-return distribution in the financial market as well as the
velocity distribution in Largrangian turbulence.
The higher order randomness (HORN) hypothesis is introduced as the
stochastic source of the cascade distribution. A leakage term from HORN
is introduced to model the covariance between large volatility and
large negative return.
A volatility model based on two SIBM processes is built to model the
volatility autocorrelation. The volatility half-times of 20 days and
300 days are extracted from the DJIA data.
The model generates the static log-return distributions from 10 days to
320 days that match the DJIA data satisfactorily. It also predicts an
alternative interpretation of the volatility smile/skew observed in the
options market. The relation between the SIBM model and the
multifractal random walk model is examined, which yields a simplified
SIBM model that could be quite useful in finance.
keywords: lognormal cascade, fat tail, volatility clustering, autocorrelation, multifractal
(
C)
2008:
Abstract:
This working paper studies the skew lognormal cascade distribution,
which is the static solution of the simplified SIBM model (Lihn 2008,
SSRN: 1149142). Both the symmetric distribution and the skew
distribution are studied.
The analytic formula of the raw moments and the cumulants are
calculated. The implication to the multiscaling property is also
studied for the symmetric distribution. The Taylor expansion on the
distributions and their logarithms are carried out.
An alternative Taylor expansion method is proposed to improve the
convergence of the power series for the numerical computation of the
probability density function. This method can be implemented via a
computer algebra system and enable the numerical algorithm to produce
high precision result.
keywords: lognormal cascade distribution, Taylor expansion, fat tail
(
C)
| Copyright (c) Stephen Lihn. Dec, 2023 |
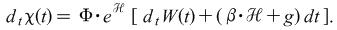 where
where
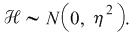
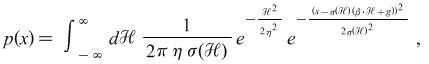
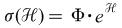
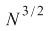 Scaling Law:
Scaling Law:
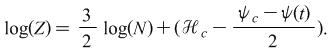
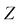 : Total market value,
: Total market value,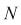 : Number of stocks,
: Number of stocks,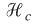 : Logarithmic mean of capital distribution
: Logarithmic mean of capital distribution
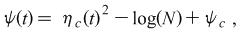
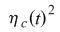 : Variance of capital distribution
: Variance of capital distribution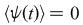 : Mean reverting volatility
: Mean reverting volatility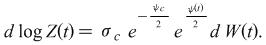
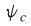 : Capital Distribution Constant
: Capital Distribution Constant
